Learning Examples | Foundations | Hacking | Links
Examples > WiFi Library
Connect With WPA
This example scans for 802.11b/g networks with the Arduino WiFi shield. Your Arduino's serial monitor will print out information about the board and the networks it can see. It will not connect to a network.
Hardware Required
- Arduino WiFi Shield
- Shield-compatible Arduino board
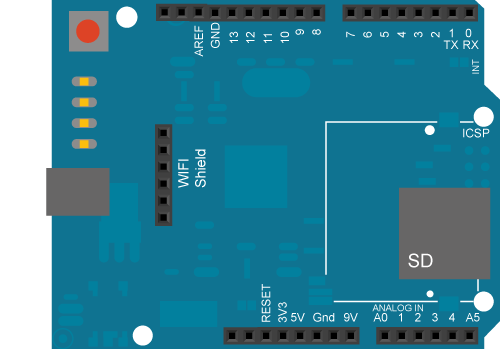
Circuit
The WiFi shield uses pins 10, 11, 12, and 13 for the SPI connection to the HDG104 module. Digital pin 4 is used to control the slave select pin on the SD card.
Open your serial monitor to view the networks the WiFi shield can see. The Arduino may not see as many networks as your computer.
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
In the above image, the Arduino would be stacked below the WiFi shield.
Code:
(:source lang=arduino tabwidth=4:) /*
This example prints the Wifi shield's MAC address, and scans for available Wifi networks using the Wifi shield. Every ten seconds, it scans again. It doesn't actually connect to any network, so no encryption scheme is specified.
Circuit:
* WiFi shield attached
created 13 July 2010 by dlf (Metodo2 srl) modified 22 April 2012 by Tom Igoe */
- include <SPI.h>
- include <WiFi.h>
void setup() {
// initialize serial and wait for the port to open: Serial.begin(9600);
// attempt to connect using WEP encryption:
Serial.println("Initializing Wifi...");
printMacAddress();
// scan for existing networks:
Serial.println("Scanning available networks...");
listNetworks();
}
void loop() {
delay(10000);
// scan for existing networks:
Serial.println("Scanning available networks...");
listNetworks();
}
void printMacAddress() {
// the MAC address of your Wifi shield byte mac[6];
// print your MAC address:
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.print("MAC: ");
Serial.print(mac[5],HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[4],HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[3],HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[2],HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[1],HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(mac[0],HEX);
}
void listNetworks() {
// scan for nearby networks:
Serial.println("** Scan Networks **");
byte numSsid = WiFi.scanNetworks();
// print the list of networks seen:
Serial.print("number of available networks:");
Serial.println(numSsid);
// print the network number and name for each network found:
for (int thisNet = 0; thisNet<numSsid; thisNet++) {
Serial.print(thisNet);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(WiFi.SSID(thisNet));
Serial.print("\tSignal: ");
Serial.print(WiFi.RSSI(thisNet));
Serial.print(" dBm");
Serial.print("\tEncryption: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.encryptionType(thisNet));
}
}
(:sourccend:)
See Also:
- ConnectNoEncryption : Demonstrates how to connect to an open network
- ConnectWithWEP : Demonstrates how to connect to a network that is encrypted with WEP
- ConnectWithWPA : Demonstrates how to connect to a network that is encrypted with WPA2 Personal
- ScanNetworks : Displays all WiFi networks in range
- WiFiChatServer : Set up a simple chat server
- WiFiPachubeClient : connect to pachube.com, a free datalogging site
- WiFiPachubeClientString: send strings to pachube.com
- WiFiTwitterClient : A Twitter client with Strings
- WiFiWebClient : Connect to a remote webserver
- WiFiWebClientRepeating: Repeatedly make HTTP calls to a server
- WiFiWebServer : Serve a webpage from the WiFi shield